Are you overweight? Do you have an appetite? Do you want to eat more, snack all the time? Do you eat too much junk food, sweets or snacks? Do you want to eat carbohydrate foods, especially at night? Are you very tired, stressed, experiencing emotional fluctuations? These symptoms may indicate that you have leptin resistance.
Leptin is the main hormone in your body; it controls hunger and satiety. Leptin is thought to play an active role in energy metabolism, endocrine system, inflammation and immune system. Leptin is secreted by adipose tissue; although it is not correct to generalize, we can say that the more weight you have, the higher your leptin levels are. Leptin release is proportional to the amount of fat in your body.
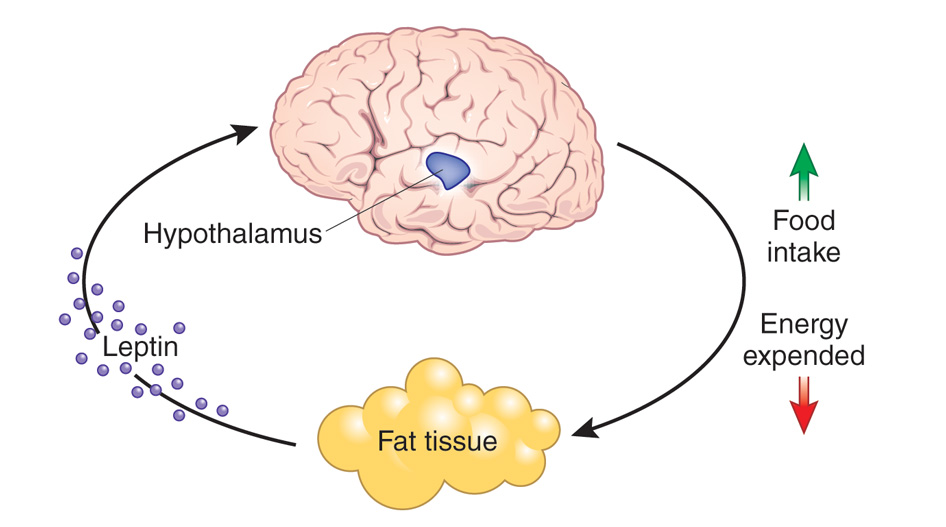
Fat cells produce leptin in proportion to their body fat level: Remember. The more fat there is, the more leptin there is. It enters the bloodstream through your circulatory system. Leptin binds with protein in the blood; when leptin reaches the brain, it crosses the blood-brain barrier and binds to leptin receptors in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. Leptin signals the hypothalamus to maintain energy balance (known as homeostasis) and increase metabolic rate. Conversely, leptin also tells you when to eat. When you have less body fat, less leptin signals the brain and sends the message “I’m hungry!”. Over time, if leptin ignores the warning signals to “eat food”, look what happens in the body: When your body’s fat levels are too high, you crave food. Studies have found that leptin resistance can also occur when you eat high amounts of fructose and are exposed to toxins or stress, which is widely believed to trigger weight gain.

Based on these research results, weight gain is associated with leptin levels. Furthermore, leptin is directly linked to insulin levels and many people today are leptin resistant. Research shows that high leptin levels increase the risk of high blood pressure, obesity, heart disease and stroke. In those who are overweight, there is leptin resistance rather than leptin deficiency. Similar to insulin resistance, these people have high levels of leptin in the bloodstream. Because leptin is constantly signaling, the body learns to ignore it; one is always hungry, the metabolic rate slows down.

Leptin Resistance
Leptin signals the brain that there is enough fat in the body and there is no need to store more fat. This prevents overeating. “So it’s a good thing that overweight people have high leptin levels, where’s the problem?” you might say. In fact, the real problem is not in leptin production; most overweight individuals who have difficulty losing weight have leptin resistance. In obese people, excess leptin is secreted from increased adipose tissue. However, this increased leptin causes a decrease in leptin-sensing receptors in the cells of the appetite center in the brain. Thus, even though there is excess leptin in the environment, the fat burning and appetite suppressing signal of leptin cannot reach the cells. This is called “leptin resistance”.

The body perceives leptin resistance as hunger, so multiple mechanisms are activated to increase fat stores instead of burning excess fat stores. Thyroid and leptin have a dangerous but significant relationship. Your thyroid secretes hormones that move throughout the body, affecting metabolism, growth and development. For example, leptin resistance can also block the effects of thyroid hormone on metabolism. The goal is not to increase leptin in the blood, but to consume leptin-sensitizing foods so that your body can better respond to its signal. In recent years, leptin has been associated with inflammation; studies have been conducted on its effect on blood CRP levels, which is an indicator of inflammation. Many diseases are known to be caused by increased inflammation in the body.

The most common factors leading to leptin resistance are:
- High levels of stress
- Simple carbohydrates (white bread, pasta, etc.)
- Inadequate sleep
- Overnutrition
- High levels of insulin
- Fructose consumption (such as corn syrup). Since it is used in many processed products, you may be consuming it without realizing it.

Here are some tips on what you can do to prevent leptin resistance:
- Basically, eat low-processed, fiber-rich, unrefined foods. You have to control your portions.
- You should limit the consumption of foods containing excess sugar and foods with a high glycemic index.
- Consume more protein and healthy fats.
- Optimize your sleep. Try not to spend time in front of the computer for 1 hour before bedtime.
- Don’t snack all the time, plan your meals
- Try getting more natural sunlight.
